Alcedinidaekingfishers(Also: kingfishers and relatives)
Diversity
Kingfishers belong to the order Coraciiformes and the family Alcedinidae. Within Coraciiformes, kingfishers are grouped into the suborder Alcidines, with todies (Todidae) and motmots (Motmotidae). Alcedinidae comprises approximately 17 genera and 91 species, and is frequently subdivided into three subfamilies; Alcedininae, which comprises most of the “fishing” kingfishers, Halcyoninae, which comprises the “forest kingfishers” that reside primarily in Australasia, and Cerylinae, which includes all of the New World kingfishers.
Kingfishers are small to medium sized colorful birds with short necks, large heads and long, thick bills. They live primarily in wooded habitats of tropical regions, often near water. Despite their name, not all kingfishers are fishing specialists. While some species do consume primarily fish, most species have unspecialized diets that include a high proportion of insects. Most kingfishers are monogamous, territorial breeders, though a few species breed cooperatively. ("Kingfishers (Alcedinidae)", 2003; Dickinson, 2003; Fry, 2003; Krueper, 2001)
Geographic Range
Kingfishers are found in all regions of the world, except in polar regions and on some oceanic islands. The majority of kingfisher species are tropical. Most kingfishers are found the Australasian, African and Oriental regions of the world, with the highest numbers in the Australasian region. Only six species, all in the subfamily Cerylinae, occur in the New World. ("Kingfishers (Alcedinidae)", 2003; Fry, 2003; Fry, et al., 1992; Krueper, 2001)
- Biogeographic Regions
- nearctic
- palearctic
- oriental
- ethiopian
- neotropical
- australian
- oceanic islands
- Other Geographic Terms
- cosmopolitan
Habitat
Most kingfishers live in forested or open woodland habitat, often near water. About 44 species live in closed-canopy forests (primary and secondary), 17 species in wooded savannas, and 31 species in aquatic habitats including seashores, mangrove swamps, lakes, rivers and streams. One species lives in desert scrub.
The main habitat requirements for kingfishers are food and nest site availability. Forest-dwelling species are generally found in the lower levels of the canopy where they forage from the forest floor. Kingfishers that require aquatic habitat can be found most often near small water bodies such as mountain streams, rivers and lakes. Most also require perches near the shore to hunt from, but a few species are able to hunt by hovering, and can forage up to 3 km from shore. Kingfishers excavate nests in earthen banks (usually), tree cavities (either natural, excavated by other animals, or excavated by the kingfishers if the wood is sufficiently rotten) or termite nests. Many kingfishers show a remarkable ability to adapt to different habitats, and may shift between very different breeding and non-breeding habitats. Kingfishers live at elevations from sea level to more than 2800 meters. ("Kingfishers (Alcedinidae)", 2003; Campbell and Lack, 1985; Clancey, 1992; Fry, 2003; Woodall, 2001)
- Habitat Regions
- temperate
- tropical
- terrestrial
- Terrestrial Biomes
- savanna or grassland
- forest
- rainforest
- scrub forest
- mountains
- Aquatic Biomes
- lakes and ponds
- rivers and streams
- coastal
- Other Habitat Features
- riparian
Physical Description
Kingfishers are small to medium sized (10 to 46 cm long, 9 to 490 g) thickset birds with large heads, short necks, short legs, and long, thick bills. They typically have rounded wings and a short tail, though eight species of paradise kingfishers have long tail streamers. Kingfishers have small, weak, 3- or 4-toed feet that are syndactyl, meaning that the front toes are all fused to some degree. The bill and feet of adult kingfishers are black or bright red, orange or yellow, and the eyes are usually dark brown. Kingfishers are generally colorful and boldly marked, often with blues and greens above and a mixture of red, orange and white below. Many species also have a pale collar and several species have a distinctive crest.
The bills of kingfishers are all long and thick, but vary in shape in accordance with the foraging habits of each species. Fly-catching species have dorsoventrally flattened bills, whereas fishing species have laterally flattened bills. Ground-feeding species, including shovel-billed kingfishers (Clytoceyx rex) usually have shorter, quite broad bills.
The sexes of most kingfisher species are similar in size and plumage, though some species show distinct differences. For example, the males of some paradise kingfishers have much longer tail streamers than females. Reversed sexual size dimorphism (females markedly larger than males) is found in the two largest kookaburra species, laughing kookaburras (Dacelo novaeguineae) and blue-winged kookaburras (Dacelo leachii). Juveniles typically look similar to adults, with somewhat duller plumage and often with mottling where adults have solid coloration.
Like motmots and todies, kingfishers often have brilliant plumage, are largely insectivorous, and nest in cavities that are often excavated in earthen banks. Kingfishers are distinguished by their long, thick, straight beak and plumage that is more often blue than green. ("Kingfishers (Alcedinidae)", 2003; Campbell and Lack, 1985; Clancey, 1992; Fry, 2003; Fry, et al., 1992; Krueper, 2001; Sibley and Ahlquist, 1990; Woodall, 2001)
- Other Physical Features
- endothermic
- bilateral symmetry
- Sexual Dimorphism
- sexes alike
- female larger
- ornamentation
Reproduction
All kingfishers are territorial. Most are also monogamous, and many pair for life. Courtship involves aerial chases, individual and joint displays, and courtship feeding. Breeding pairs emphatically defend a territory using calls and displays, which can include spiraling flight displays or displaying boldly marked plumage by perching high within the territory and spinning slowly around a vertical axis. Kingfishers actively defend their territory, chasing intruders and when necessary, grappling in the air, sometimes toppling to the ground or into the water where the fight continues. Particularly aggressive neighbors may even enter the nest cavities of one another to puncture eggs. Territory size varies between species and with food abundance and nest site availability. Where nest sites are particularly scarce, a few species of kingfishers will breed in loose colonies and defend only an area immediately surrounding the nest hole.
Some species of kingfishers are cooperative breeders. In these species, a male and female pair has one to several “helpers” that help defend the territory and feed the chicks. Helpers can be primary (related) or secondary (unrelated). They are often young from previous broods that may help at the nest for several years, and can dramatically increase nestling survival in some cases. Polygamy is known to occur in at least one species of kingfisher; male common kingfishers (Alcedo meninting) in Russia frequently breed with up to three females. ("Kingfishers (Alcedinidae)", 2003; Clancey, 1992; Fry, 2003; Fry, et al., 1992; Krueper, 2001; Woodall, 2001)
- Mating System
- monogamous
- polygynous
- cooperative breeder
Details of the breeding biology of many kingfishers are unknown. Most kingfishers that have been studied begin breeding at one year old, and can raise one to four broods per year. The female lays 2 to 10 (usually 3 to 6) white, unmarked eggs that weigh 2 to 12 g each. Eggs are laid approximately one day apart, and incubation begins either when the first egg is laid, or after the majority of eggs have been laid. The naked and blind chicks hatch synchronously in species where incubation does not begin until most or all eggs have been laid, and asynchronously in species where incubation begins with the first or second egg. Siblicide is common in the latter. Nestlings fledge three to eight weeks after hatching, and are dependent on the parents for supplemental food for several days to weeks after fledging. In most species, the adults eventually force the fledglings to leave their territory. The timing of breeding varies considerably within this family. Generally, kingfishers in temperate regions breed during the spring and summer. Those in tropical regions can breed year-round or seasonally during the time of highest prey availability.
Most kingfishers normally rear one brood per year. However, under favorable conditions, some species may rear up to four broods per year. In some cases, the male may even begin digging a new nest tunnel before the young of the previous clutch have fledged.
Kingfishers nest most often in earthen banks such as those along rivers or lakes, but they also use termite nests and tree cavities. Tree cavities made by other species, such as woodpeckers, are readily used. If these are not available, kingfishers will excavate a cavity in wood (if it is sufficiently rotten), or another substrate. The male and female excavate the cavity together, taking turns pecking and scraping material with their bills and feet. Several species begin excavation by flying bill-first into the surface, an occasionally fatal strategy. The tunnel to a kingfisher nest cavity may be as long as three meters. The cavity is slightly larger in diameter than the tunnel, and is not lined with any material. Nest cavities can take up to a week to excavate, and pairs often use the same nest hole for many years. ("Kingfishers (Alcedinidae)", 2003; Clancey, 1992; Fry, 2003; Fry, et al., 1992; Krueper, 2001; Woodall, 2001)
- Key Reproductive Features
- iteroparous
- seasonal breeding
- year-round breeding
- gonochoric/gonochoristic/dioecious (sexes separate)
- sexual
- fertilization
- oviparous
Both male and female kingfishers incubate the eggs, which take 2 to 4 weeks to hatch. During the nestling stage, which lasts 3 to 8 weeks, both parents feed the young regurgitant, and later whole prey items. During the last part of the nestling stage, parents may feed each chick as frequently as once every 15 minutes. When the nestlings are large enough to fly, the parents may withhold food for a few days to encourage the chicks to leave the nest. After the chicks have fledged, the parents provide supplemental food while the chicks learn to hunt for themselves. Some kingfishers also teach their young to hunt. For example, belted kingfishers (Megaceryle alcyon) drop dead prey into the water for their young to practice diving. After up to three weeks of supplemental feeding, adult kingfishers usually force their young to leave their territory.
Adult kingfishers do not engage in any nest sanitation, such as removing feces from the nest cavity. Because most kingfisher nests have only one outlet, nests can become rather smelly and are often infested with maggots as feces from the chicks and food scraps accumulate. ("Kingfishers (Alcedinidae)", 2003; Fry, et al., 1992; Krueper, 2001; Woodall, 2001)
- Parental Investment
- altricial
- male parental care
- female parental care
Lifespan/Longevity
Kingfishers are thought to be relatively long-lived, but survival and longevity unknown for most species. Adult annual survival is thought to range between 25 and 55 %. A common kingfisher (Alcedo atthis) is among the oldest known kingfishers at 15 years and 5 months. A captive laughing kookaburra (Dacelo novaeguineae) also lived over 15 years. Sources of kingfisher mortality include predation, collection, and collision with man-made structures such as windows, towers and building during nocturnal migrations. (Fry, 2003; Krueper, 2001; Woodall, 2001)
Behavior
Most kingfishers live as solitary breeding pairs that defend a territory year-round. Several species defend their territory to the extent that they attack other species, including other birds, goannas (Varanus), weasels (Mustela nivalis), dogs and cats. A few species, such as pied kingfishers (Ceyx lecontei) and laughing kookaburras (Dacelo novaeguineae) are cooperative breeders. In these species, cooperative groups, which include a breeding pairs and one to several helpers defend a territory together. At night, most kingfishers roost alone on a perch within their territory. During incubation, females may roost in the incubation chamber.
Most species are sedentary, but about a few species are migratory or partially migratory. Unlike many bird species, some kingfishers migrate during the day. All but one species of kingfishers are diurnal. The nocturnal species is hook-billed kingfishers (Melidora macrorrhina), which feed largely at night. Many species are inactive during the hottest part of midday.
Many species of kingfishers have been observed bathing by diving repeatedly into water. Kingfishers generally preen frequently, and anting has been observed in at least one species of kookaburra. ("Kingfishers (Alcedinidae)", 2003; Fry, 2003; Krueper, 2001; Woodall, 2001)
Communication and Perception
Kingfishers have very good eyesight, and rely heavily on sight for hunting. Their eyes have two fovea, which allow them to very accurately judge the distance to a prey item by turning their head slightly. Their eyes are also especially rich in oils that enhance color vision. At least one species of kingfisher is able to see near UV light. When some kingfishers dive for fish, their eyes are covered by a nictitating membrane. This means that these species must rely on their sense of touch to know when to snap their bill closed in order to catch the fish.
Kingfishers are highly vocal species that used calls to advertise their territory and to communicate between family members. Some pairs of kingfishers call in duets, and cooperative groups of kookaburras call in a chorus at dawn and dusk. While the vocalizations of most species are not well studied, those species that have been studied often have several different vocalizations. For example, belted kingfishers (Megaceryle alcyon) use at least six calls in various combinations to convey messages. Several species also produce non-vocal sounds, such as bill rattling. ("Kingfishers (Alcedinidae)", 2003; Fry, 2003; Woodall, 2001)
Food Habits
Despite the name of this group, not all kingfishers are fish specialists. Many kingfishers are unspecialized carnivores that are often largely insectivorous, and may take prey from the ground, the air, water or foliage. Kingfishers are highly adaptable, and will generally take whatever prey is available. Their diets can include a variety of insects (frequently grasshoppers), reptiles (skinks, snakes), amphibians, mollusks, non-insect arthropods (centipedes, millipedes, scorpions, spiders, crabs), mice, and even small birds. Those species that are fish specialists usually also include some insects in their diet. One species of kingfisher has been seen eating carrion, and a few species occasionally eat berries or the fruit of oil palms. Kingfishers can take prey that are large relative to their body size. For example, laughing kookaburras can take snakes up to 1 meter long, though the tail may protrude from their bill for a time while the head end is digested.
The “fishing” kingfishers for which this group is named, can dive up to two meters below the surface of the water to catch fish. Some have a nictitating membrane that covers and protects their eyes as they enter the water, which means that they must anticipate the movements of their prey before they enter the water, and rely on their sense of touch to determine when to snap their beak shut. Other feeding specialists among the kingfishers include shovel-billed kingfishers (Clytoceyx rex) which use their beak to plough through earth and leaf-litter, looking for earthworms, grubs, snails, centipedes and lizards. Ruddy kingfishers (Halcyon coromanda) in the Philippines remove land snails from their shells by smashing them against stones on the forest floor. A few species follow other animals (including otters, platypus, cormorants, egrets, cattle or army ants) to catch prey that they disturb. Some species also attend grassfires to catch prey that are scattered by the flames. Kleptoparasitism has been reported in several species; the victims included blackbirds, song thrushes, water shrews, hawks and tree snakes.
The majority of kingfisher species hunt from a perch, surveying quietly for prey, and swooping down to surprise it. A few species search for prey while flying, and a few others forage on the ground. Most species catch prey by surprising it, and rarely chase prey for any length of time. Once a kingfisher catches a prey item, it carries it to a perch (often the same one from which it was hunting) and uses its beak to beat the prey item against the perch until it is soft enough to swallow whole. This preparation removes the legs and wings of insects and breaks the bones, protective spines, and shells of fish, crustaceans and other prey. ("Kingfishers (Alcedinidae)", 2003; Fry, 2003; Fry, et al., 1992; Woodall, 2001)
- Primary Diet
-
carnivore
- eats terrestrial vertebrates
- piscivore
- insectivore
- eats non-insect arthropods
- molluscivore
Predation
There are relatively few records of adult kingfisher predation. Kingfishers are quick fliers, and probably able to escape most predators. Most known predators of adult kingfisher are raptors. Nest predators include foxes, minks, dingoes, skunks, raccoons, chimpanzees, snakes , monitor lizards, driver ants, and mongooses.
When threatened, kingfishers seem to employ one of two strategies; they either try to evade the predator by dodging behind trees or diving into the water, or they attack the predator directly, mobbing it until it leaves the area. A few species have alternative strategies; yellow-billed kookaburras raise their head feathers when threatened, revealing two black spots that resemble large eyes. When alarmed, young red-backed kookaburras assume a posture with their eyes closed and their beak pointed upward that make them look like the limb of a tree from above. Kingfishers aggressively defend the nest area against nest predators, often attacking intruders including humans. (Woodall, 2001)
- Anti-predator Adaptations
- mimic
-
- Known Predators
-
- owls (Strigiformes)
- foxes (Vulpes)
- minks (Mustela)
- dingoes (Canis lupus dingo)
- skunks (Mephitinae)
- raccoons (Procyon lotor)
- chimpanzees (Pan)
- snakes (Serpentes)
- monitor lizards (Varanidae)
- driver ants (Formicidae)
- mongooses and relatives (Herpestidae)
Ecosystem Roles
As predators of various species, kingfishers affect the populations of their prey. Most species of kingfishers are not parasitized by brood parasites, but a few in Africa are hosts for greater (Indicator indicator) and lesser honeyguides (Indicator minor). (Woodall, 2001)
Economic Importance for Humans: Positive
Kingfishers are collected for sale to tourists, or for their bright plumage, which is used in traditional costumes of some societies. (Woodall, 2001)
- Positive Impacts
- body parts are source of valuable material
Economic Importance for Humans: Negative
Kingfishers sometimes take privately owned fish from fish farms or garden ponds. (Woodall, 2001)
Conservation Status
The biggest threat facing most kingfisher populations is the destruction or alteration of their habitat by logging, pollution of water bodies and development. Significant numbers of kingfishers are also killed by shooting, collision with cars and buildings, and accidental poisoning from pesticides and poisons intended for other species. While it appears that many species of kingfishers are relatively adaptable to changes in habitat, the biology of most species is not well known, making conservation planning or prediction of impacts to habitat difficult.
The IUCN lists 1 kingfisher species as “Endangered”, 11 as “Vulnerable”, 12 as “Near-threatened”, and 3 as “Data deficient”. No kingfisher species are listed under any CITES Appendices. In the United States, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service lists one species, the Guam Micronesian kingfisher (Halcyon cinnamomina cinnamomina) as endangered. Four species are protected by the Migratory Bird Treaty Act. ("UNEP-WCMC Species Database: CITES-Listed Species", 2003; IUCN, 2003; Threatened and Endangered Species System, 2003; U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, date unknown; United States Department of Agriculture, 2002; Woodall, 2001)
-
- IUCN Red List [Link]
- Not Evaluated
Other Comments
Fossils of kingfishers from as early as 40 million years ago have been found in Wyoming (USA). ("Kingfishers (Alcedinidae)", 2003)
Contributors
Alaine Camfield (editor), Animal Diversity Web.
Kari Kirschbaum (author), Animal Diversity Web.
Glossary
- Australian
-
Living in Australia, New Zealand, Tasmania, New Guinea and associated islands.
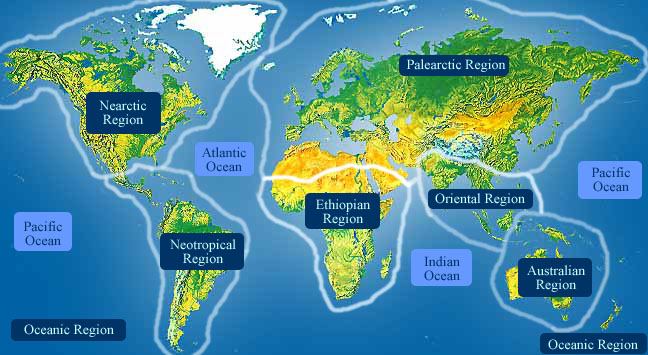
- Ethiopian
-
living in sub-Saharan Africa (south of 30 degrees north) and Madagascar.

- Nearctic
-
living in the Nearctic biogeographic province, the northern part of the New World. This includes Greenland, the Canadian Arctic islands, and all of the North American as far south as the highlands of central Mexico.

- Neotropical
-
living in the southern part of the New World. In other words, Central and South America.

- Palearctic
-
living in the northern part of the Old World. In otherwords, Europe and Asia and northern Africa.

- acoustic
-
uses sound to communicate
- altricial
-
young are born in a relatively underdeveloped state; they are unable to feed or care for themselves or locomote independently for a period of time after birth/hatching. In birds, naked and helpless after hatching.
- bilateral symmetry
-
having body symmetry such that the animal can be divided in one plane into two mirror-image halves. Animals with bilateral symmetry have dorsal and ventral sides, as well as anterior and posterior ends. Synapomorphy of the Bilateria.
- bog
-
a wetland area rich in accumulated plant material and with acidic soils surrounding a body of open water. Bogs have a flora dominated by sedges, heaths, and sphagnum.
- carnivore
-
an animal that mainly eats meat
- chemical
-
uses smells or other chemicals to communicate
- choruses
-
to jointly display, usually with sounds, at the same time as two or more other individuals of the same or different species
- coastal
-
the nearshore aquatic habitats near a coast, or shoreline.
- cooperative breeder
-
helpers provide assistance in raising young that are not their own
- cosmopolitan
-
having a worldwide distribution. Found on all continents (except maybe Antarctica) and in all biogeographic provinces; or in all the major oceans (Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific.
- diurnal
-
- active during the day, 2. lasting for one day.
- duets
-
to jointly display, usually with sounds in a highly coordinated fashion, at the same time as one other individual of the same species, often a mate
- endothermic
-
animals that use metabolically generated heat to regulate body temperature independently of ambient temperature. Endothermy is a synapomorphy of the Mammalia, although it may have arisen in a (now extinct) synapsid ancestor; the fossil record does not distinguish these possibilities. Convergent in birds.
- female parental care
-
parental care is carried out by females
- fertilization
-
union of egg and spermatozoan
- forest
-
forest biomes are dominated by trees, otherwise forest biomes can vary widely in amount of precipitation and seasonality.
- insectivore
-
An animal that eats mainly insects or spiders.
- internal fertilization
-
fertilization takes place within the female's body
- iteroparous
-
offspring are produced in more than one group (litters, clutches, etc.) and across multiple seasons (or other periods hospitable to reproduction). Iteroparous animals must, by definition, survive over multiple seasons (or periodic condition changes).
- male parental care
-
parental care is carried out by males
- marsh
-
marshes are wetland areas often dominated by grasses and reeds.
- migratory
-
makes seasonal movements between breeding and wintering grounds
- molluscivore
-
eats mollusks, members of Phylum Mollusca
- monogamous
-
Having one mate at a time.
- motile
-
having the capacity to move from one place to another.
- mountains
-
This terrestrial biome includes summits of high mountains, either without vegetation or covered by low, tundra-like vegetation.
- native range
-
the area in which the animal is naturally found, the region in which it is endemic.
- nocturnal
-
active during the night
- oceanic islands
-
islands that are not part of continental shelf areas, they are not, and have never been, connected to a continental land mass, most typically these are volcanic islands.
- oriental
-
found in the oriental region of the world. In other words, India and southeast Asia.

- oviparous
-
reproduction in which eggs are released by the female; development of offspring occurs outside the mother's body.
- piscivore
-
an animal that mainly eats fish
- polygynous
-
having more than one female as a mate at one time
- rainforest
-
rainforests, both temperate and tropical, are dominated by trees often forming a closed canopy with little light reaching the ground. Epiphytes and climbing plants are also abundant. Precipitation is typically not limiting, but may be somewhat seasonal.
- riparian
-
Referring to something living or located adjacent to a waterbody (usually, but not always, a river or stream).
- scrub forest
-
scrub forests develop in areas that experience dry seasons.
- seasonal breeding
-
breeding is confined to a particular season
- sedentary
-
remains in the same area
- sexual
-
reproduction that includes combining the genetic contribution of two individuals, a male and a female
- sexual ornamentation
-
one of the sexes (usually males) has special physical structures used in courting the other sex or fighting the same sex. For example: antlers, elongated tails, special spurs.
- social
-
associates with others of its species; forms social groups.
- solitary
-
lives alone
- swamp
-
a wetland area that may be permanently or intermittently covered in water, often dominated by woody vegetation.
- tactile
-
uses touch to communicate
- temperate
-
that region of the Earth between 23.5 degrees North and 60 degrees North (between the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle) and between 23.5 degrees South and 60 degrees South (between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle).
- terrestrial
-
Living on the ground.
- territorial
-
defends an area within the home range, occupied by a single animals or group of animals of the same species and held through overt defense, display, or advertisement
- tropical
-
the region of the earth that surrounds the equator, from 23.5 degrees north to 23.5 degrees south.
- tropical savanna and grassland
-
A terrestrial biome. Savannas are grasslands with scattered individual trees that do not form a closed canopy. Extensive savannas are found in parts of subtropical and tropical Africa and South America, and in Australia.
- savanna
-
A grassland with scattered trees or scattered clumps of trees, a type of community intermediate between grassland and forest. See also Tropical savanna and grassland biome.
- temperate grassland
-
A terrestrial biome found in temperate latitudes (>23.5° N or S latitude). Vegetation is made up mostly of grasses, the height and species diversity of which depend largely on the amount of moisture available. Fire and grazing are important in the long-term maintenance of grasslands.
- visual
-
uses sight to communicate
- year-round breeding
-
breeding takes place throughout the year
References
2003. Kingfishers (Alcedinidae). Pp. 5-10 in M Hutchins, J Jackson, W Bock, eds. Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia, Vol. 10. Detroit: Gale Group.
2003. "UNEP-WCMC Species Database: CITES-Listed Species" (On-line). Accessed March 26, 2004 at http://www.cites.org/eng/resources/species.html.
Campbell, B., E. Lack. 1985. A Dictionary of Birds. Vermillion: Buteo Books.
Clancey, P. 1992. Kingfishers of Sub-Saharan Africa. Johannesburg: Jonathan Ball and AD. Donker Publishers.
Dickinson, E. 2003. The Howard and Moore Complete Checklist of the Birds of the World, 3rd edition. London: Christopher Helm.
Fry, C. 2003. Kingfishers. Pp. 366-371 in C Perrins, ed. The New Encyclopedia of Birds. Oxford: Oxford Univeristy Press.
Fry, C., K. Fry, A. Harris. 1992. Kingfishers, Bee-eaters and Rollers. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press.
IUCN, 2003. "2003 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species" (On-line). Accessed March 26, 2004 at http://www.redlist.org/.
Krueper, D. 2001. Kingfishers. Pp. 370-372 in C Elphick, J Dunning, D Sibley, eds. The Sibley Guide to Bird Life and Behavior. New York: Alfred A. Knopf.
Sibley, C., J. Ahlquist. 1990. Phylogeny and Classification of Birds, A study in Molecular Evolution. New Haven: Yale University Press.
Threatened and Endangered Species System, 2003. "U.S. Listed Vertebrate Animal Species Report by Taoxonomic Group" (On-line). Accessed March 26, 2004 at http://ecos.fws.gov/tess_public/TESSWebpageVipListed?code=V&listings=0#B.
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, date unknown. "Birds Protected by the Migratory Bird Treaty Act" (On-line). Accessed March 26, 2004 at http://migratorybirds.fws.gov/intrnltr/mbta/mbtintro.html.
United States Department of Agriculture, 2002. "Integrated Taxonomic Information System" (On-line). Accessed March 26, 2004 at http://www.itis.usda.gov/.
Woodall, P. 2001. Family Alcedinidae (Kingfishers). Pp. 130-187 in J del Hoyo, A Elliott, J Sargatal, eds. The Handbook of the Birds of the World, Vol. 6. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions.




